How to Create an Internal Communication Strategy: Step-by-Step Guide & Template
Successful Internal Communication Planning
An internal communications strategy defines business goals in communicating with employees and plans the activities to achieve these goals. It's the blueprint guiding you to internal communications success.
Creating this strategy involves some work, but there are clearly defined steps to follow along the way.
We’ve developed a four-step process for creating your own custom internal communications strategy, whatever your organization’s size or sector.
Download Internal Communication Strategy Template
Why Do You Need An Internal Communications Strategy?
An internal communications strategy is important because it strengthens the connection between employees, employers, and the company's mission.
It increases commitment by keeping employees informed. It boosts productivity by raising employee engagement. And it drives business success by maximizing the effectiveness of every activity.
An effective internal communication strategy will inform, engage, and improve your organization.

- Audiences - Collect information on the composition of your organization. This should include number of staff, locations, departments, demographics, devices used and any other factors related to your organizational structure.
This information can then be used later for audience segmentation to deliver targeted, highly relevant messages – key to achieving greater readership and response. - Environmental Influences - Consider which issues, needs and challenges are influencing your communications. Is it difficult to communicate with staff working in certain environments, such as call centers, warehouse or frontline retail? What specific messaging needs do different departments have?
Consider the table below. How many of the issues outlined currently afflict your organization? How significant is the impact of each? What value to your organization would resolving each offer?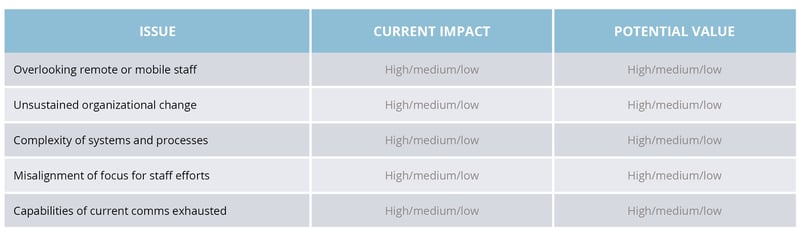
- Current Communications - Understand how your current internal communications have been performing and what level of employee engagement has been achieved.
Review your existing comms toolset. Which current channels are the most effective? Are certain channels more effective for specific types of messages? What types of messages are your existing channels not well suited to?
2. Goals & Objectives: Where Do You Want To Be?
Now that you know your current situation, you can begin to plan what you want it to be. This step is about defining your objectives and ensuring alignment with overall company direction.
- Future Focus - Start with your vision for the future of internal communications in your organization. How does it look – is it a centralized IC function or decentralized by location or functional area?
- Business Goals - Internal communication is most effective – and most valuable – when it aligns with overall business goals.
Consult your organization’s business plan for details on KPIs and core projects at both company and departmental levels. This will provide you with useful information on where to expend your internal communications efforts. - Communication Priorities - Now you know what the primary business objectives are, you can start to form your communication priorities.
Consider what response you want staff to have to your communications. This could either be a physical action or an emotional change – that is, a response of act vs feel. - Setting Objectives - When you come to set objectives, be specific about what you want to achieve. Is it a hard metric, such as ‘Achieve 100% readership of all important announcements within 60 seconds’? Or is it a softer metric, such as ‘Increase employee engagement by 25%’?
There are many different techniques for effectively setting objectives. One of the most common is to set SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-Bound).
Many businesses are now taking that a step further and setting SMARTER goals, which add Evaluate and Readjust at the end to reflect the importance of continual improvement.
Here are some quick tips for setting successful communication objectives - and mistakes to avoid.
- Ensure communication goals ladder up to company goals - internal comms is most effective when it's focused on driving the business forward
- Make sure you can measure results - if you can't track and report on the outcome of your efforts you'll never know whether they worked or not (and you can't showcase your successes to management!)
- Review last year's goals first - knowledge of prior performance can suggest areas to focus on and activities to repeat
- Set achievable goals - it's fine to create BHAG (Big Hairy Audacious Goals) to motivate staff, but if they're too unrealistic they can risk being discouraging
- Summarize goals clearly - short, simple and succinct statements make them memorable
3. Planning: How Will You Get There?
This step is where the best tactics and most effective communication channels are combined to achieve your objectives.
- Communication Tasks - Make a list of all the main communication tasks scheduled for the year. Each task will require a tailored internal communications plan. Then map these tasks across your annual employee communication calendar.
Start with your company's essential communication tasks, such as daily health and safety talks, cybersecurity training, quarterly employee surverys, and open enrollment. Work with other departments such as IT, marketing, HR, and legal to support their communication campaigns. - Audience Targeting - Segment your employees into distinct groups based on their working environment or communication preferences. Set these groups up in your communication platforms to enable easy targeting of relevant messages – in the format and channel best suited to them.
Consider the following table for the audiences relevant to your organization. Putting yourself in the shoes of your audiences will help you to better understand their needs and then deliver to them through targeted, relevant message solutions.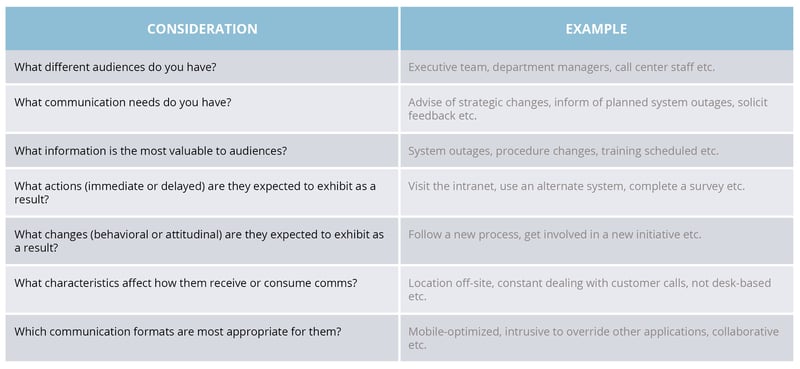
- Contingency Plans - Create a contingency plan that outlines alternative courses of action to be taken in the event of roadblocks to the main plan. Whether timing delays, lack of resources, or inclement weather. Preparing back-up messages in advance can help reduce stress when obstacles arise, as well as allow you to act more swiftly in response.
- Channel Selection - The type of content you need to communicate, and the urgency with which staff must consume it, will help define the most appropriate channels.
For example, communicating IT outage notifications, promoting campaign events, and soliciting feedback for company announcements all have very different purposes – and require very different communication channels.
It’s advisable to use multiple channels to maximize the best attributes of each and reduce the risk of relying on a single, overloaded channel. The key is balance, variety, accessibility, and repetition.
Here are a few communication best practices for channel selection:
- Multiple touches – Reaching audiences at different times, in different environments
- Multiple formats – Combining text, imagery, or video engages audiences more
- Short burst, bite-sized – Quick to read, understand, and act upon
- Repetition – Recall improves as message exposure increases
- Disruptive and passive formats – High-visibility notification and discreet reinforcement
- Templates – Faster message creation and consistent branding
4. Measurement: How Will You Know If It Worked?
The final step is about tracking results and implementing a cycle of continuous improvement.
- Measurement - Put systems in place to track how achievement is progressing against your objectives. What’s working well – and, more importantly, what isn’t?
Delve into the data to identify improvements that can be made immediately.
There is a range of different KPIs you can use to measure performance. These include open rates, click-through rates, survey response rates, number of comments and shares, engagement levels, and device types used. - Testing - Try different approaches to see if one is more successful. For example, send the same message with two different subject lines to see which has the higher open rate. Or deliver content in text vs visual formats to see which has better engagement.
In Marketing, this is referred to as A/B testing. Insights gleaned through testing will help your quest to construct the perfect message. - Two-way Feedback - Be open to requesting, collecting, and reporting on employee feedback. Mechanisms such as staff sentiment surveys and intranet forums can be fertile ground for honest and helpful views.
- Evaluate and Evolve - Use channel tracking and analytics tools to identify which channels have been more successful. Revisit your strategy on a quarterly basis to evaluate how it's working. Share the results and how these are supporting wider company performance with the rest of the organization.
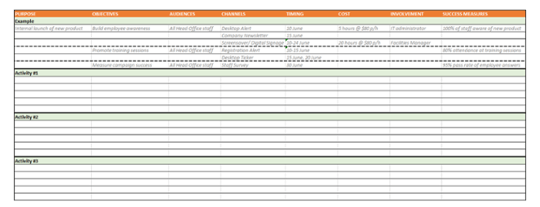
Internal Communication Strategy Template
Download our internal communications strategy template for examples, tips, and best practices to create a successful program of internal communications – from concept to completion.
Download The Template
An internal communication strategy is a structured plan that outlines how an organization communicates with its employees. It defines goals, messages, channels, and methods to ensure effective, consistent communication that supports business objectives and fosters employee engagement. It's the blueprint guiding you to internal communications success.
An effective internal communication strategy keeps employees informed, aligned with the company’s goals, and motivated. It improves engagement, boosts productivity, enhances team collaboration, and ensures vital information reaches the right people at the right time.
Common channels include email, intranet platforms, video conferencing tools, internal newsletters, digital signage, messaging apps, desktop alerts, desktop tickers, and employee apps. The choice of channels should be based on employee preferences and the nature of the messages.
A strategy focuses on long-term goals and defines the overall vision for internal communication. A plan is a detailed outline of the specific tactics and actions needed to implement the strategy in the short term.
The key components include:
- Objectives aligned with business goals.
- Audience segmentation and understanding.
- Message clarity and relevance.
- Selection of appropriate communication channels.
- A feedback mechanism to track effectiveness and improve.